
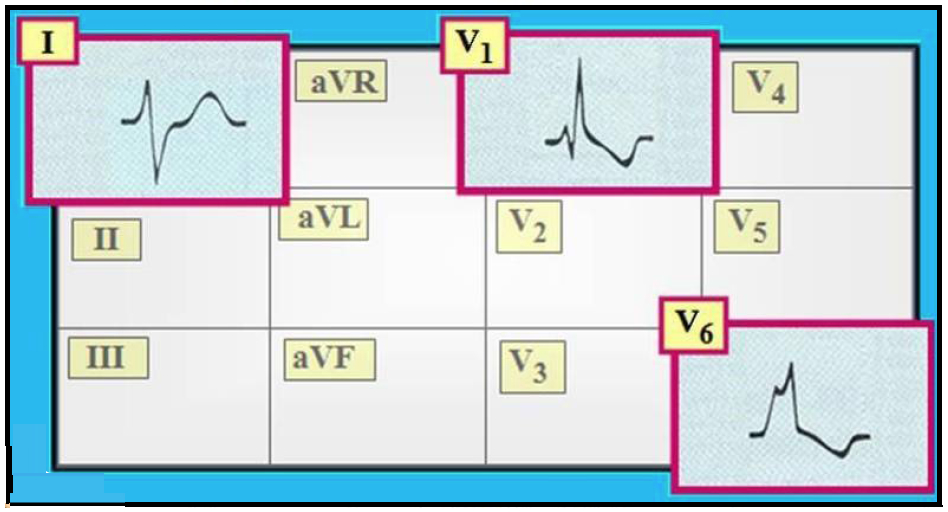
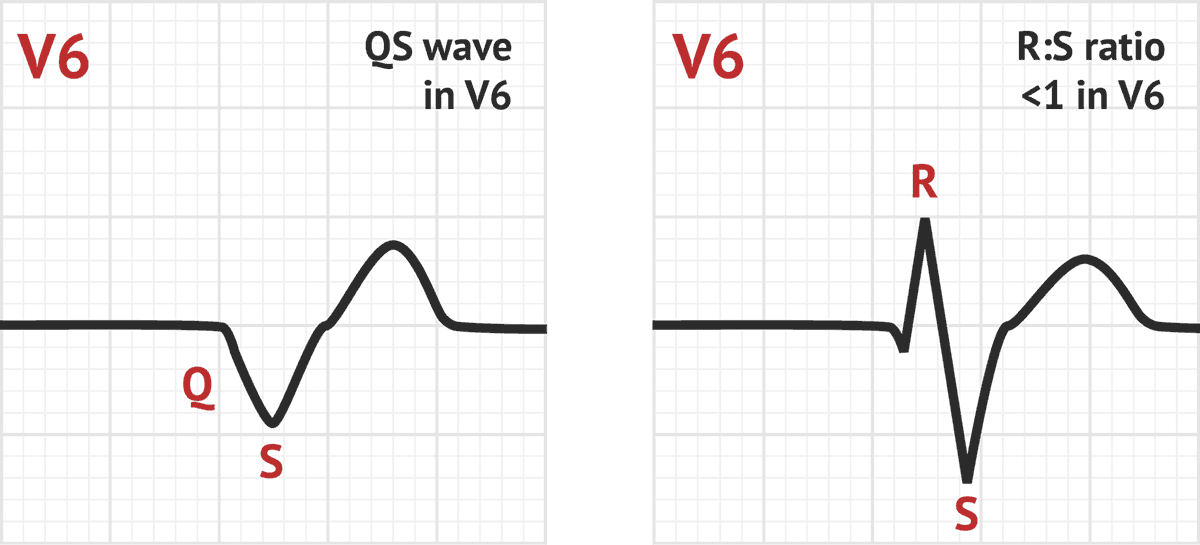
However, these alerts often have a high false-positive rate, due to the artifacts mentioned above. Conduction in RBBB: With a blockage in the right bundle branch (red), the left ventricle is excited in time (purple), while the excitation of the right ventricle takes a detour via the left bundle branch (blue arrows). For example, VTach, VFib, Asystole, and AFib are commonly detected by telemetry equipment and reported to personnel in the form of audible and visual alerts. However, IVCD is often used to denote a wide QRS that does not have a classic LBBB or RBBB. Differential Diagnosis of RBBB An RSR’ pattern in V1-3 may also be caused by Brugada syndrome an ECG pattern associated with malignant ventricular arrhythmias. It is a normal variant, commonly seen in children (of no clinical significance). The right bundle branch block morphology is atypical (monomorphic R. Incomplete RBBB is defined as an RSR’ pattern in V1-3 with QRS duration < 120ms. Real telemetry monitoring systems do include more advanced features not seen here, such as dynamic warning of dangerous rhythms. LBBB and RBBB waves, as well as more atypical morphologies. Given atrial fibrillation and RVH one should strongly consider mitral stenosis. In addition, back pain is an atypical complaint in patients with. This also wreaks havoc on the automated rhythm warnings generated by telemetry systems! Regardless of the type of right bundle branch block, the ECG patterns remain similar. Many factors such as electrode placement, body weight, movement, muscle tremors, shivering, or even pacemakers can cause the EKG signal to become noisy or difficult to read. I have attempted to pick cleaner samples for this site in general, but real patients cause a lot of what we call "artifacts" on EKG monitors. Additionally, the "baseline" of the EKG (which should be at 0 voltage or the exact center of the chart) can also change or vary depending on conditions. You can see just how much amplitude changes from patient to patient simply by looking at samples here. This sometimes requires "zooming in" in order to better see important details. Depending on the patient, electrode placement, and other factors, the amplitude (or height) of the waves can change dramatically. Real telemetry monitors also allow you to adjust the speed and amplitude of the EKG waves. LBBB and RBBB were identified according to standard definitions (QRS duration > 120 ms). This unique format allows for easy analysis of cardiac rhythms. Telemetry monitors have a unique plotting style, "drawing" the EKG wave across the screen, then overwriting the wave on the next pass. Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs) exist in this encounter as well. Also present is a right bundle branch block (RBBB). Rhythm analysis indicates a borderline normal sinus rhythm (NSR). With this, the reader can really see if the basic c- cepts and ECG fundamentals have been learned.The experience between watching EKGmon and a hospital telemetry monitor is very similar. Patient is being monitored during a mitral valve replacement and coronary artery bypass graft procedure. Khan includes an invaluable section-an ECG Board Review and Self- Assessment Quiz. This is f- lowed by a chapter with each of the arrhythmias. After reviewing each component of the ECG, the next section describes the unique ECG patterns of speci? c cardiac conditions, including pulmonary embolism and long QT syndrome. IVCD is defined as a QRS complex >110 ms that does not have morphological features consistent with either LBBB or RBBB. This quickly orients the reader to the physiology, anatomy, and geometry of the electrical system of the heart. Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is found more commonly in HCM than in athletes but the frequency of incomplete and complete RBBB in athletes is felt to limit its differentiating value.23, 30 The significance of a non-specific intraventricular conduction delay (IVCD) with normal QRS morphology is uncertain. This edition includes a new opening chapter that covers basic concepts. This, as many of us have been taught, is the “right” way to look at an ECG. More imp- tant, it takes a step-by-step approach, walking the reader through a thorough evaluation of the ECG. Rapid ECG Interpretation is comprehensive, yet concise, and very practically oriented. So, what would we want from a book on ECGs? Ideally, such a book would be comprehensive, yet concise, practically oriented, and explain pathophysiology and its application to practice.
Learning the basics and subtleties of the ECG is a right of passage for all physicians and healthcare providers during their training. Thus, for any phy- cian, a solid understanding of the ECG is critical. The electrocardiogram (ECG) is the ? rst test performed on most cardiac patients–one that helps make the ? rst part of the diagnosis and one that can frequently direct treatment decisions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
